Ready Mixed Concrete Management System
POROShbs Solution in Ready Mixed Concrete Management
BSOFThbs Ready Mixed Concrete Management System
and Application Architecture
BSOFThbs is a ready-mixed concrete software developed to provide automation in the ready-mixed concrete sector, developed with a modern management information system and up-to-date technologies that will instantly and regularly monitor productivity with a central control system. It is designed to meet all the needs of concrete companies serving in one or more regions.
Application Architecture
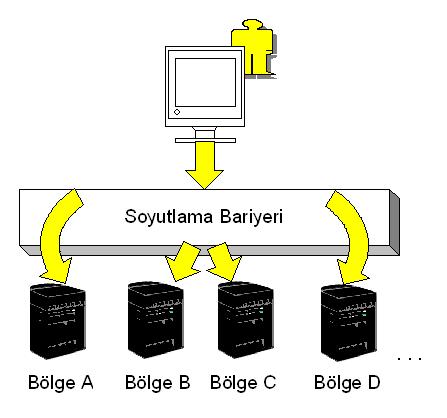
The architecture of BSOFThbs Ready Mixed Concrete Management System can be divided into two as software and hardware architecture. Without dwelling on the main lines of the software architecture, it is useful to mention the hardware structures it supports. BSOFThbs Ready Mixed Concrete Application has an effective hardware control architecture that can run on a single server as well as control the distributed information structure that occurs in companies with multiple servers.
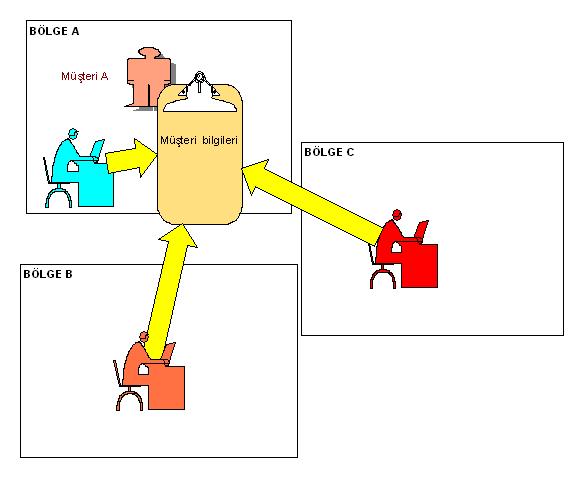
One of the most important problems encountered in companies with a regional structure is the difficulties in sharing information arising from the dispersed structure of the company. BSOFThbs brings a solution to this problem. It also provides easy access to information in different regions. Any user in any region, if he has the authoritycan access all company-wide information as if it were the information of its own region.
Structures in the System
Company Organization
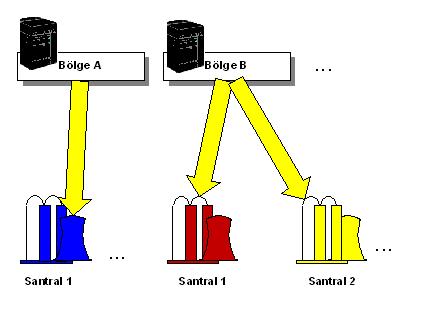
BSOFThbs company structure is designed as a concrete company, Regional Directorates affiliated to this company, and plants affiliated to Regional Directorates. In addition, the areas where the plants sell are divided into price zones.
Customer Structure
A single customer number is used for each customer, even if the customer works in multiple regions. The customer is considered to be the customer of the region in which the customer first started working, and the Debit / Credit transactions that will occur in other regions and switchboards are collected in the region where the customer first works.
Detail accounts of customers can be monitored separately under a single account number. Where the total debit-credit of the customer can be seen, the debit-credit of the detail accounts can also be seen separately. For example, accounts such as Sales, Unrecoverable maturity difference, etc. can be monitored separately, as well as the total debt, receivable, risk, credit, collateral information of the customers can be monitored.

Contract structure
Contracts with customers are stored with expiration date or other control parameters (such as quantity, amount).
The contract may provide for special prices for certain products, may be tied to certain forms of sales, may be valid for certain construction sites.
Special notes can be included in the contract.
Special discounts and maturity difference rate to be applied to the customer, special pump price can be specified.
Discounts can be made on a contract basis.
Construction site structure
The customer’s construction in any province or district is introduced to the system as a construction site. Each construction site is given a code. Customers’ construction sites are entered into the system:
- Working Hours,
- Shipment Address,
- Invoice Address,
- Distance
- Special Notes
- Switchboard
- Power Plant Price Zone,
- Transport Region,
- When referral is not appropriate
is introduced with information such as.
Construction sites can be closed for any reason.


Forms of sale
Any number of sales types can be defined in the system. In this definition, the payment time and discount rate of the sale can be specified. While specifying the payment time, standard days such as 7 days, 10 days, 1 month… etc. can be defined, or special definitions can be made such as those received during the month should be paid on the last day of the following month, those received between 1-10 of the month should be paid on the 30th day of the month.
Shipment Methods
For concrete sales; Pumped? With mixer? For cement sales; Bag or bulk? Bulk can be distinguished.
Delivery Methods
It can be distinguished whether the sale is a power plant delivery or a construction site delivery.
Price Structure
The system tracks concrete sales separately as product and pump prices, and cement and crushed stone sales separately as product and transportation prices. Transportation is created according to transportation regions. Price information is kept separately as price circulars. Price queries can be made retrospectively. Price circulars include circular date, circular validity start date, delivery method, region, power plant and power plant price zone information.
Product Prices
Product prices are kept as circulars with price start dates. Sales prices for power plant delivery and construction site delivery are introduced separately. When searching for a price, the system first checks whether there is a special price in the person’s contract, if not, it takes the current price on the order date from the circulars. Prices can be defined according to region, power plant and power plant price zone. Defining new circulars can be done automatically based on old circulars.
Example:
Zone……………….: 01 Zone A
Switchboard …………….: 01 Switchboard A
Price zone ……..: 1 Price Zone A
……………..: B225 Concrete A
Price at ……………….: 8.000 TL

Pump Prices
If the pump prices are specified in the contract, the contract pump price, if not, the pump is delivered according to the m3 ordered at the latest valid prices in the pump price circular. Pump prices can also be questioned retrospectively. For example; 120.- TL up to 50 m3, 100.- TL above.
Transportation Prices
In cement and crushed stone sales, prices are indicated on the basis of transportation region. Transportation prices are kept in the form of transportation price circulars. The system recognizes which transportation region the construction site is in and finds the current price. These prices can be changed on order basis.
User Definitions
The region and switchboard personnel of the users are introduced to the system. In daily operations, it works with the information of its own switchboard unless otherwise requested.
Guarantees
The types of collateral accepted in the concrete company (letter of guarantee, cash, stocks, etc.) are defined. Then, for each customer, the collaterals received are entered into the system with the date of receipt, type, description, validity date, collateral amount and accepted rate (credit forming) information.
The applicable rate or amount of the collateral amount is specified. The collateral amount is calculated by the system according to the specified rate or amount.

General Features
- It can be installed on Server or PCs (Client) depending on demand and need.
- The database is always located on the Server. There is no information storage on the Client side.
- Parametric Infrastructure.
- User or role-specific menu design can be made.
- Data can be sorted, grouped, filtered and stored by column.
- User-specific screen views can be made and stored.
- Support for multiple workplaces and branches.
- It has integration with office programs.
- Authorization can be done on user and role basis.
- Uses MS SQL server for data management.
- There is no data loss or corruption whatsoever.
- It can be installed and used in Client/Server or terminal server structure.
- It has an automatic backup system.
- It has a log system. All additions, changes and deletions made in BSOFThbs are logged. Easily reported.
- It offers unlimited reporting possibilities. In addition to the dozens of reports it contains, BSOFThbs allows the user to prepare and add the desired report to the structure thanks to the reporting program it contains.
- Thanks to the filtering structure in the reports, the user can access the different analyses and graphs he/she desires.
- Reports can be archived as exel, XML or text if desired.

BSOFThbs Modules and Functions
BSOFThbs includes the following modules. And you can use these application modules integrated with each other or independently.
- General Parameter and Definition Operations,
- Current Account Transactions,
- Inventory Operations,
- Order Processing,
- Laboratory Operations,
- Sales Operations,
- Maintenance Operations,
- Vehicle Tracking Operations,
- Actual Cost Transactions,
- Standard Cost Operations,
- Budget Operations,
- Check Processing,
- General Accounting Transactions,
- Fixed Asset Transactions,
- Personnel Transactions,
Vehicle Tracking and Maintenance Module: POROSHBS_TB
One of the most important issues that companies with a large number and variety of vehicles have difficulty in is to keep the daily movements of their vehicles, fuel purchases and most importantly, maintenance periods under control. Keeping the vehicles under careful and accurate observation plays an important role in determining the efficiency of the vehicle as well as the user personnel, i.e. drivers.
The Vehicle Tracking / Maintenance module, also known as POROSHBS_TB, which has been developed integrated into the POROSHBS Ready Mixed Concrete Management System package, serves to ensure that the vehicles within the company can be used effectively, efficiently, reliably and without interrupting the work. With the magnetic projections of the vehicles, which are an indispensable part of the general operation, interventions that increase the cost efficiency can be made instant and reliable. The operations associated with each vehicle in the vehicle pool are generally as highlighted below.
General Information Definitions
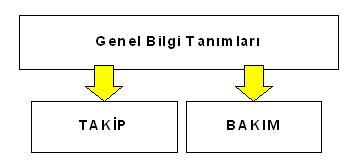
POROSHBS_TB Vehicle Tracking/Maintenance module consists of two main sub-modules as the name suggests:
- Vehicle Tracking
- Vehicle Maintenance.
Information to be referenced for both Tracking and Maintenance can be defined through General Information Definitions, which are common to both modules.
The purpose of the General Information Definitions is to ensure that the definition of the information that is likely to be grouped is realized once and that definitions are made to increase the accuracy and reliability of the information to be entered by in-house users during use. In this way, the selected working method will not restrict the operations to be carried out for the tracking and maintenance of the vehicles, and with the controls it brings, transactions contrary to the operating rules determined by the company will be prevented.
General Information Definitions
and Vehicle Grouping
General Information Definitions focus on the main concepts listed below.
1.) Vehicle Grouping
- Vehicle Types
- Vehicle Classes
- Vehicle Types
2.) Movement Scenarios
Tool Grouping :
Vehicles should be grouped according to their common characteristics. The purpose of grouping is to avoid repeated definitions for each vehicle in the same group with common characteristics. There are three different filters that distinguish a vehicle from other vehicles: type, class and type of vehicle. For the vehicles whose classes are created by grouping, a set of common definitions and rules are made once and for all vehicles in this group.
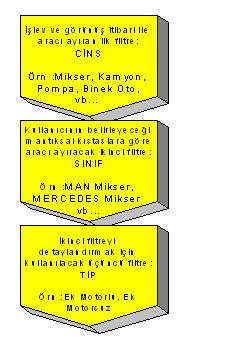
The figure below is given as an example of grouping and does not include any mandatory classifications that must be defined in any company. Concepts such as VEHICLE-A, VEHICLE-B, RENTED are used for example, and POROSHBS_TB users can open and use any grouping class or type they want. There is no problem or restriction in terms of number as well as concept.
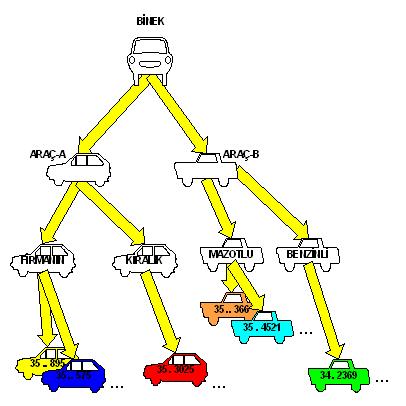
When we look at the example figure above, it is possible to say the following for 35 . For 3025 it is possible to say the following.
Type of 35.3025: RIDE
Class : VEHICLE-A
Type : FOR RENT
This means that the tool automatically includes all common definitions and rules defined for this group.
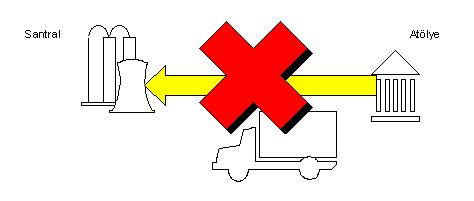
Movement Scenarios
If you don’t want too many vehicles to make it difficult to control, if you want to know where the vehicle I want is right now, who is the driver; POROSHBS_TB is the answer to your problem.
With the movement scenarios to be prepared, it is possible to model the movements that can be performed for all vehicles included in a group. What is meant by modeling here should be understood as determining the movements that the vehicle can perform one after the other.
Physically, it is not possible to prevent the movements of a vehicle except for internal rules. However, controlling the opening of records in accordance with these rules in the computer environment and preventing possible errors in record entries requires such a modeling. For example, it would be possible to prevent the filling of concrete into a mixer in the workshop for troubleshooting with movement scenarios. Or it will be impossible for a passenger vehicle to make an entry movement to the filling.
Movement scenarios are defined under vehicle groups. In this way, it is not necessary to specify which action can be performed and which cannot be performed for each vehicle individually. For Mixers, the figure below shows how to make it impossible for a mixer that is under repair in the workshop to enter the filling with movement scenarios.
Documents
Modules
Current Account Transactions
In addition to grouping your current accounts (Vendor, Customer, Bank, etc.), it is an application where you can follow your current accounts on the basis of detail account (sales, unpaid, maturity difference…etc.), get instant statements, aging reports and as a result, you can easily manage all finances. Debit and credit records from the integration are automatically reflected to current accounts.
The delivery notes issued from the sales program are immediately debited to the current account with the payment date. When the invoice is issued, these delivery notes are deleted from the current account and debited on invoice basis.
Checks/notes entered from the Checks/Notes program are immediately processed to the current account with their due dates. At this stage, automatic debt settlement is performed. Debt settlement is performed from the oldest debt according to the specified account priority (for example, bad debts first, then due date debts).
Other debts and receivables are processed manually from the current program and automatic debt settlement is performed at this stage.
In this application, debit/credit aging reports of customers according to transaction date, maturity date and/or vendor registration number can be obtained company-wide and on a plant basis.
Total detailed receivable reports, collection reports received in accordance with the due date, received before due date, received after due date, average maturity, average discount reports can be obtained throughout the company and/or on the basis of power plant region/substation.
Customers’ debts/receivables, due and overdue debts, from which power plants and how much in total can be monitored.
Current card transactions
– You can define current account cards as alphanumeric and numeric, get detailed and cumulative reports
– You can include current cards in different groups as you wish and get reports based on these groups.
– You can define any number of detail accounts on a single current card and get all reports based on these accounts.
– You can enter transactions to a current card in different currencies at the same time and get all the desired reports.
– You can enter detailed population information on current cards, follow bank accounts and special information about the card.
– You can define a placement code for current cards and track risk and customer transactions on placement basis.
– You can define account-specific calendar codes in current card details and track payment days and currencies.
– You can follow the bank, branch and account details of the current account.
Current movement transactions
– You can enter current transactions in different currencies.
– By defining transaction codes with different properties and names, you can also track transaction details on the basis of transaction type.
– You can match the debts and receivables of current transactions according to the criteria you want and get maturity difference, debt / receivable analysis reports.
– Debt settlement and receivable settlement options can be used optionally with the settlement transaction programs.
– Open debts can be tracked with closing information control reports.
Current account movement reporting operations
– You can report current card transactions in different currencies according to transaction codes.
– You can follow the latest status of your company from a single report by getting a general debit / credit trial balance.
– You can quickly access the summarized information you want with the help of the summary reports.
– You can track customer collection and risk thanks to current account aging reports.
Current accounts collateral transactions
– You can retrieve the collateral information received based on the current card.
– By defining different collateral types, you can get summary reports for collateral types.
– Thanks to the collateral warning lists, you can get the report of collaterals whose expiration date is approaching.
– You can track collateral types (Cash, Check, Promissory Note, Bank collateral).
– You can get collateral reports according to banks.
Inventory Operations
It is a Windows-based application where you can define an unlimited number of warehouses, units and flexible levels of stock cards, and at the end of the month, you can automatically cost and report according to the desired price tracking method. You can quickly make recipe definitions, counting operations and transfers between warehouses.
You can define stock cards by giving them as many levels as you want and collect them under different groups. You can define an unlimited number of warehouses and units and report your stocks according to these definitions (warehouses, units, etc.). You can quickly make counting transactions, counting difference receipts, transfers between warehouses, prescription definitions of the product. You can automatically make costing at the end of the month according to the desired price tracking method and get reports.
General Characteristics
- You can define stock cards by giving them as many levels as you want and you can group them under different groups.
- In stock cards, you can define minimum/maximum stock levels, minimum order quantity, economic order quantity, average lead times, width, length, height, packaging information, shelf life, etc., as well as barcode definitions (used in the company, sales, purchasing, etc.).
- You can define an unlimited number of warehouses, locations and units and report your stocks according to these definitions (warehouses, locations, units, etc.).
- You can quickly make counting transactions, counting difference receipts, transfers between warehouses, and recipe definitions for finished goods.
- At the end of the month, you can automatically make costing according to the desired price tracking method and get reports.
- You can define accounting integration definitions at the desired level as stock card, main group, subgroup and general, and you can make stock and accounting integration in a parametric way.
Stock card operations
- You can define an unlimited number of auxiliary units in addition to the main unit in stock cards and get all your reports based on the defined units.
- You can define stock card groups in any number and breakdown you want.
- You can get detailed and cumulative reports thanks to the groups defined on stock cards.
- You can follow the details of stock cards such as width, length, height, packaging information.
- For stock cards, you can follow the barcodes specified in sales and purchases by defining them separately.
- You can define recipes with different characteristics of the product.
- In addition to the minimum and maximum stock quantities defined for stock cards, you can track order quantity, economic order quantity, shelf life and average lead time.
Inventory Receipt Operations
- You can duplicate stock movement codes in any number and type.
- You can specify the default properties of Entry-Exit-Transfer transactions according to the created transaction types. You can make quick entry during receipt transactions.
- You can track stock statuses on warehouse and general basis and get stock statuses in all warehouses on a single report.
- Thanks to the color codes in the receipt entry program, the general characteristics of the receipts entered can be determined from the screen.
- You can track the user information of the user who entered and modified the receipt.
- You can define stock accounting accounts at the level you want as stock card, main group, subgroup and general, and you can make accounting integration in a parametric way.
Inventory reporting
- Thanks to the parametrically prepared inventory reports, you can get reports in the detail you want.
- You can create all reports in different units defined on the stock card.
- You can get your stock quantity in all warehouses in a single report, or you can get all movement reports in a single warehouse.
- You can get inventory inventory reports by grouping according to different movement types.
- Inventory reports can be received consistently and quantitatively in main groups.
Counting operations
- You can perform counting operations repeatedly on the dates you want.
- You can create count reports according to different criteria. You can get pre-count and post-count reports.
- By entering the results of the counting you have done, you can automatically create counting surplus and deficit receipts.
Order Processing
It is a 100% windows-based application where you can manage the entire process from the receipt of ready-mixed concrete orders from customers, technical and financial approval processes to delivery to the construction site.
Separate orders are taken for each plant. Orders can be taken to customers of other regions. During order taking, the order program and vehicle status on the day the delivery is requested can be monitored. The authorization of the person placing the order, the suitability of the construction site for the desired date, special warnings for the construction site, special warnings for the customer, contract duration, control parameters, special warnings about the contract are checked by the system and the user is warned if necessary.
Definitions such as new customer, new construction site of the customer, new contract, new payment method can be made at the order stage if the user is authorized. It can be specified that the order received from any power plant will be delivered from another power plant. Orders can be taken for another power plant. During the order, the system finds the prices and payment methods from the contract information but can change them. The date the order is received, the date and time the customer wants it to be delivered and the date and time the company can deliver it are kept. Then, if there is a gap in the delivery schedule, deferred orders can be tracked and shipped.
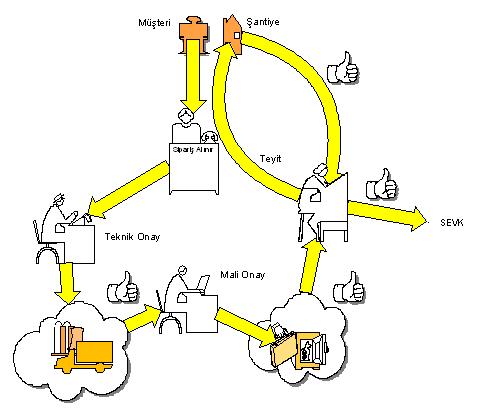
During the order processing, the system refers to the following three approval authorities and in the absence of approval, the order will not be shipped.
Technical Approval
The technical managers confirm that the order will be shipped on the specified date. The technical approval takes into account vehicle condition and technical capacity. If no approval is given, the shipment will not be made.
Financial Approval
After examining the customer’s current account and credit status by the financial officers, approval is given if there is no contrary situation. If approval is not given, the shipment will not be made.
Confirmation
Before the shipment day of the order, the customer’s construction site is called by phone and notified that the order will be delivered. It is learned whether the construction is ready or not. At the same time, the possibility that the order is unfounded or given by an unauthorized person is checked.
The order may be closed in some justified cases. In these cases, shipment will not be possible.
Laboratory Operations
It is an application where the strength tests of concrete samples taken from the plants where ready-mixed concrete production is made, data is kept and reporting is made. Statistical data is created for the concrete class in the requested periods.
Sieve tests are performed with samples taken from purchased raw materials and their conformity to standards is examined. These raw materials are also checked for compliance with the ratios given for the concrete to be produced and compliance with TSE standards. The program shows whether the determined ratios are within the sieve curve or not, and a recipe is created within the concrete class with these ratios.
Dispatch and Sales Operations
It is an application in which the orders whose approvals and confirmations are given are shipped according to the plan, and sales invoices, as well as maturity difference and special invoices are issued to the delivery notes in certain periods.
DISPATCH (WAYBILL)
Orders that have been approved and confirmed can be shipped. Orders of another plant can be shipped from one plant. Shipments can be made to other regional customers.
When the dispatch note is issued, all information except quantity, vehicle code and driver comes automatically from the order.
After the PCs in the plant, which control the production, receive the “Cut delivery note” command from the servers, the specified product is produced by the PC in the specified quantity. After the production is completed, the delivery note is printed on the printer and the raw materials used for production are deducted from the stock. The cost of the delivery note is automatically processed to the current account and debt settlement is done instantly. If the customer is in remote region, the program debits the current account in that region. The shipment amount is deducted from the order amount.
When communication is interrupted, the PC stores the production made and the amount of raw materials used. When the connection is made, the delivery notes issued from the PC are transferred to the server. At this stage, the information stored in the PC is processed in the necessary modules (stock, current etc.).
INVOICE
Product Sales Invoice
Invoices can be issued in certain periods (e.g. 10 days) to the dispatch notes that have been issued. Invoices can be issued to all dispatch notes issued in the company at once, or invoices can be issued by selecting region, plant, customer, construction site, shipment method, delivery method, product group, payment method. Collective invoice drawing can also be done as a draft for control purposes. The system issues a separate invoice for each construction site and payment method of the customer. It collects invoices with the same characteristics in a single invoice (according to the number of delivery notes).
When the invoice is issued, the system discards the waybills that have been processed to the current account, writes the invoice instead, and makes the debt settlement automatically in the same way. If the invoice is canceled, the invoice is deleted from the current account, the waybills come back. The same waybills can be invoiced again.
Due Difference Invoice
The system calculates and displays to the user the interest rate difference according to the interest rate specified in the customer’s contract from the debt settlements in the current accounts of the customers. The user can change the interest rate difference amounts if they wish. By selecting the desired customers, only those customers can be invoiced for the interest difference.
Special Invoice
Allows invoices such as service invoices, etc. to be issued from the computer, except for sales and credit invoices.
Invoice Offset
Invoices are selected by date or number and automatic offset is created.
Sales Reports
Various detailed and summary views and reports can be obtained according to the criteria of region, plant, customer, construction site, product, shipment method, delivery method, payment method, shipment date, invoice date, order date.
Order shipment comparison reports can be obtained.
When the report programs run, it detects that the region, switchboard or customer is on the remote machine and brings the information to that machine via line connection if necessary.
Maintenance Operations
Pre-detection of malfunctions that may occur in vehicles and the best way to repair them, periodic maintenance and control of vehicles, and efficient tracking of breakdown repair and maintenance costs are carried out with the POROSHBS_TB Vehicle Maintenance module.
- Malfunctions
POROSHBS_TB allows grouping of faults based on vehicle types. This kind of grouping will help to create a fault database. Thus, when a malfunction is encountered, the operations to be performed, the materials to be checked and their equivalents can be brought to the repairer. The repairer, who automatically accesses the information about the failure, can easily learn what to do even if it is the first time he/she encounters the failure. It is aimed to reduce the risk in repair and increase the reliability of repair.
- Failure Notifications
Another important factor in resolving faults easily and efficiently is the detection and repair of faults without undesirable consequences. For this purpose, the Fault Reporting facility provided by POROSHBS_TB enables vehicle users to record any faults they feel or suspect. Even if they do not come face to face with the repairers, they can convey their suspicions to the repairers.
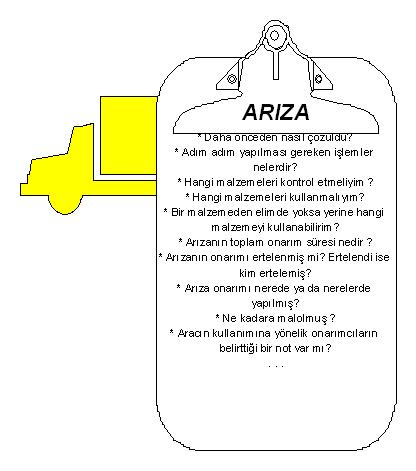
- 3) Workshop and External Repair Shop
POROSHBS_TB module calls the repair centers where repairs are performed within the company as workshops, and the external commercial centers that perform repairs as external repair shops. Depending on the malfunctions, it can be prevented or required to perform repairs in workshops or external repair shops.
- Repairs / Maintenance Performed
For completed repairs or maintenance, it is possible to enter information about the personnel who completed the repair or maintenance, the materials used, the cost incurred, the time taken for completion, the personnel who confirmed that the repair was completed, and the actions taken. Repair or maintenance completions will also lead to increased knowledge about the repairs or maintenance. For example, if a material that was not previously included in the list of materials to be used for the repair/maintenance was used in the repair/maintenance, this material will be shown to the repairer in the list of materials that can be used in the next repair or maintenance of the same type. Knowing the repair times plays an important role in determining the efficiency of the workshop or external repair shop.
- Maintenance
Maintenance definitions performed on the basis of vehicle groups include a list of materials to be used or checked, as well as a list of operations to be performed as in the case of malfunctions.
- Maintenance Periods
Maintenance periods can be defined on the basis of vehicle groups. Maintenance periods are defined based on kilometer, cycle or date intervals. With the maintenance period definition, it is aimed to perform the maintenance of the vehicles on time. With POROSHBS_TB alerts, upcoming or past maintenance vehicles are displayed and the maintainers are notified.
- Retrospective Maintenance and Breakdowns of Vehicles
Answers to questions such as “Which vehicle has which malfunctions frequently?”, “Which vehicles have been out of service for how long for maintenance or repair?”, “Which maintenance requires how long?”, etc. can be easily accessed to increase vehicle usage and cost efficiency.
POROSHBS_TB contains effective inquiries for making decisions that are directly related to the total cost of the vehicle, such as replacing or selling vehicles, purchasing new vehicles, replacing one or some of the accessories of the vehicles.
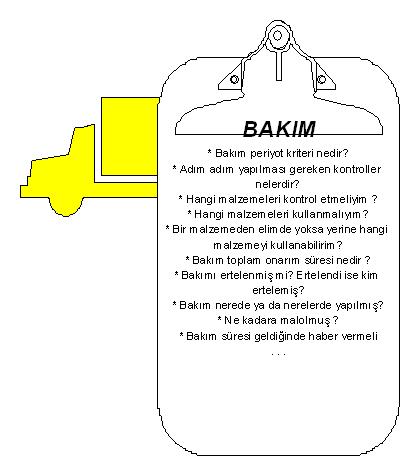
- Vehicle Repair/Maintenance Life Cycle
Sometimes the process of repairing a malfunction or completing a maintenance operation involves more than one movement of the vehicle. For example, a vehicle is towed to a workshop for repair. If the repairers in the workshop cannot fix the fault, they can send it to an external repair shop. The external repair shop can solve the problem or send it to another external repair shop. Or some external repair shops may be competent in certain areas and others may be competent in other areas. To complete the repair or maintenance, the vehicle may need to travel between workshops and de/ or external repair shops. For example, the painting may be carried out by workshop A, but the engine check may be carried out by workshop B.
A second possibility is that breakdowns or repairs are postponed by authorized personnel. All vehicle movements during the repair or maintenance period, including such postponements, constitute the repair/maintenance life cycle of that vehicle.
The following figure shows the vehicle’s tasks that need to be completed
- A Troubleshooting
- B Troubleshooting
- Painting the vehicle
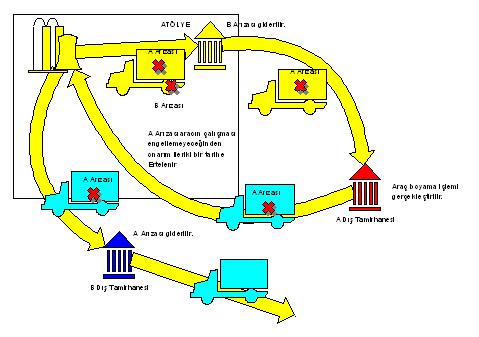
B It is determined that the defect can be repaired in the workshop and the repair is carried out in the workshop. The vehicle leaving the workshop completes the painting process at the A exterior repair shop. Repair of Defect A is postponed when it is decided that Defect A does not affect the operation of the vehicle for a while or when the external repair shop B gives a date for a future date. If Fault A is a fault that will not prevent the vehicle from starting, the vehicle is allowed to start. If the fault is of a nature that may prevent operation: POROSHBS_TB would shut down the vehicle and not allow it to run. When the postponement time expires, the repair of Defect A is completed in the external repair shop B.
The figure shows only an example scenario and POROSHBS_TB remains in control, no matter how complex the movements.
- Fault Resolution Management in Connection-Required Systems
In companies with multiple server systems, the security of the distributed structure of information must be kept under control. POROSHBS_TB Error Recovery Management is constantly activated to prevent loss of data in case the connection is interrupted during the process. The user is made to feel as if the necessary data flows between the systems even if there is no connection. When the connection is restored, the data is automatically transferred between the relevant systems.
Vehicle Tracking Operations
The Vehicle Tracking sub-module aims to control the movement, cost and utilization of any vehicle owned by the company for more efficient use.
1) Vehicle Power Plant
Companies with more than one power plant can assign their vehicles to power plants. While tracking the vehicles whose responsibilities are separated according to the power plant, the power plant personnel will only be interested in the vehicles that fall under their responsibility, and they will be able to see the vehicles of other power plants if they wish and if they have authorization. This will increase the reliability of information and will bring along a number of additional advantages such as ease of operation, increased efficiency and prevention of errors.
However, requirements sometimes lead to vehicles being used in different plants. POROSHBS_TB allows the use of vehicles between plants with the process called Transfer. It will be very easy to determine in which power plant a vehicle is located at any desired time or time period, different information in different power plants will be shown only to authorized users, and the responsibility of that vehicle will be easily assigned to the power plant users with an abstraction barrier created. Since it is unlikely that vehicles that are not physically present at the plant site will be able to enter the filling area, the vehicle’s switchboard will provide an effective control so that the control of the vehicle to be filled can be carried out correctly.
2) Vehicle Movements:
The relocation of vehicles from one place to another, which requires time, fuel and personnel, i.e. resources. vehicle movement is called. Vehicle movements are kept under control based on movement scenarios determined on the basis of vehicle groups. Based on these scenarios, the movements that each vehicle can perform are also defined.
Vehicle movement includes the start and end location as well as the functional state of the vehicle. For example, whether the mixer is full or not. With this information, it is possible to find out where a vehicle is at any given time and which concrete pouring operation it is involved in. With the POROSHBS_TB query modules, the current position of the vehicle is instantly displayed.
3) Fuel Oil :
One of the most needed information for efficiency monitoring and fault detection of vehicles is the amount of fuel they burn. This requirement necessitates effective fuel tracking. Fuel can be acquired in two different ways. The first is the fuel providers owned by different organizations, which we define as external gas stations. The second is in-house gas stations if the company has its own fuel pumps. Tracking the external gas stations and the purchases made from the relevant external gas stations will facilitate the tracking of payments related to these companies.
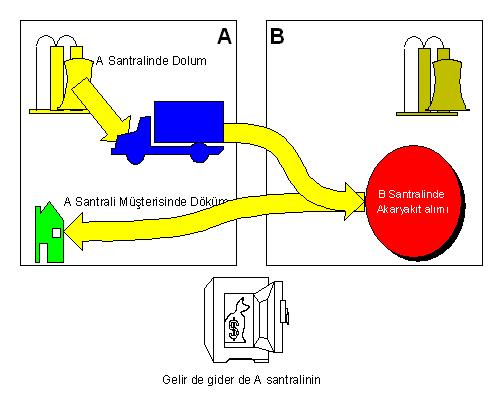
Tracking of in-house gas stations is important in reflecting the cost of fuel purchased from different plants to the vehicle’s own plant in in-house fuel purchases, which play an active role in inter-plant efficiency calculations. Such a need will be understood when a vehicle in plant A purchases fuel from plant B while pouring concrete for a customer for plant A. Because while the concrete pouring of the vehicle should be recorded as income to plant A, the fuel consumed should be recorded as expense, but since the control is not performed effectively in such purchases, the expense is recorded to plant B. POROSHBS_TB eliminates this problem and ensures that income and expense are reflected to the real plant.
The fuel expenditures of the vehicles can be analyzed and any problems that may exist in the vehicle can be detected before the problem grows. It is possible to control the fuel consumption of vehicles indexed to mileage or speed.
Attempting to analyze the fuel consumption of special vehicles such as mixers directly by mileage may lead to erroneous conclusions. It’s called a campaign and it’s called a defined sequence of movements that the vehicle must perform for casting to the customer It is not forgotten that the additional parts of the vehicle are also working during the process we call as “fuel consumption”. This additional work causes the vehicle to consume more fuel than the odometer reading. POROSHBS_TB allows you to automatically find the actual fuel consumption of the vehicle by taking into account the consumption that may result from this additional work.
The odometer malfunction during fuel purchases is also taken into account.
- Vehicle Radios
Control of radios on vehicles or in control centers is ensured.
- Tires
Tire types and brands, the vehicles in which the tires are used are all possible with POROSHBS_TB. Detailed tire tracking can be done up to which tire is mounted in which position of the vehicle.
- Visa, Vehicle Stamp Controls
Legal obligations such as visas and vehicle stamps can be checked quickly and easily. Vehicles with expired visas can be monitored quickly.
- Driver (Personnel)
It is easy to check who was driving the desired vehicle at the desired time period. Accessing retrospective information and identifying the driver of the vehicle will answer many difficult problems. Knowing the drivers using the vehicles plays an important role in the calculation of personnel efficiency. Which drivers use the vehicles better and more efficiently can be easily understood through query programs. Naturally, inefficient, bad or malicious use will not be overlooked. Concrete pours per driver can be observed.
- Concrete Filling and Waybill
The vehicle filled with ready-mixed concrete goes to the customer with the delivery note. The vehicle to be filled with concrete has a number of features. First of all, it must be present at the plant site, it must not be defective or in maintenance or closed for any other administrative reason. Such rules applied in normal operation must also be supported by the computer environment. POROSHBS_TB is fully integrated with the delivery note module. Vehicles are automatically checked for suitability for filling. This prevents filling of wrong vehicles and issuance of delivery notes. At the same time, if there is only one vehicle suitable for filling in the plant area, the delivery note is automatically issued on that vehicle (unless otherwise specified).
- Order Shipment Planning
One of the most important factors that increase the profitability of ready-mixed concrete organizations is effective shipment planning. Companies with more than one plant should be able to use their vehicles between plants in the most appropriate and fastest way according to the order dispatch plan. POROSHBS_TB contains queries that will ensure the most effective use of vehicles in this sense. It is as easy as pressing a button to see how many vehicles are in which power plant, how many of them are out of order or in maintenance.
- Mileage / Tachometer tracking
It will be possible to keep the last and current mileage of the vehicle under constant observation with the mileage or transfer times obtained during different movements such as fuel purchase, vehicle delivery, vehicle transfer.
- Insurance
Insurance policies of vehicles can be tracked via POROSHBS_TB.
Actual Cost Operations
It is an application where you can extract costs on the basis of power plant and company-wide costs according to their stages and automatically send distribution and cost receipts to accounting. Cost related values are automatically retrieved from the modules that make up POROShbs (sales, inventory, vehicle, etc.).
In this application, the costs realized on plant basis and company-wide are extracted according to their phases. Related distribution and cost receipts are prepared for accounting.
The program distributes the expenses incurred throughout the company to the power plants and the expenses incurred in the power plants to the expense locations according to the rate, amount, amount or key specified by the user. Distribution can be made from an expense location within the power plant to other power plants.
Some realized values are brought from sales, inventory, vehicle tracking programs. The user has the possibility to change these values.
For the allocation of vehicle-related expenses, idle capacity calculation is made and the expenses of vehicle backlog in one plant are allocated to other plants according to certain keys.
Plant-based phase costs and total costs can be monitored.
1) Monitoring Costs
Phase Cost : It is possible to monitor the costs of the phases listed below.
- Raw material
- Production,
- Distribution,
- Cost of Concrete without Pump,
- Pump Cost,
- General Administration,
- Sales Marketing,
- Total Concrete Cost
The phases can be varied by the user. For example ‘Plant delivery concrete cost’.
Unit costs can also be accessed using production information.
Fixed and variable costing can be done.
It is possible to monitor stage costs proportionally.
Monitoring the details of the phases; it is possible to group the expenses and access information according to the expense groups and, if desired, it is possible to go more detailed and access information up to the value of the expense incurred for the phase.
The quantities of expenses that are quantified in accounting, the usage amount and average price for unit production quantity can be monitored. This is especially important for monitoring raw material costs.
Costs can be monitored company-wide or separately by power plants.
It is possible to compare the costs of the plants.
It works integrated with accounting.
2) Idle Capacity
A vehicle in every power plant does not mean that it is used in that power plant. Although there are many vehicles belonging to a power plant, these vehicles may be used in many power plants during the day. Therefore, in order not to unfairly inflate the costs of central plants with a large number of vehicles, we calculate the number of vehicles based on the cost.
3) Distribution Receipt of Automatic Auxiliary Expense Places
Distributed Expense Locations (Auxiliary Expense Locations): It is the name given to the production expenses incurred throughout the company in systems where there are more than one power plant and power plant-based cost is desired to be monitored.
If more than one power plant caused these production costs, each power plant should be allocated a share in the calculation of power plant costs in proportion to its share in the generation of these costs. By fairly allocating the production costs to the cost centers in the power plants, it is possible to calculate the real profit on a plant basis. Examples of the allocated expense locations are: Laboratory, Workshop, Head Office Mixer, Pumps, Silobuses. Various information is utilized for the distribution of auxiliary expenses to power plants. We can summarize this information as follows.
3.1) Number of Vehicles Based on Cost
It works integrated with vehicle tracking. By using the number of vehicles based on the cost calculated with the idle capacity, it ensures that the distribution to the power plants is made in these ratios. The following criteria are utilized in distributions:
- Number of pumps
- Number of mixers
- Total number of vehicles
3.2) According to Vehicle Kilometers
It works in integration with Vehicle Tracking/Maintenance and distribution is carried out according to the mileage values made at each power plant.
3.3) Number of Personnel
It works integrated with the personnel and realizes the distribution of expenses according to the number of personnel of the power plants. The following criteria are utilized.
- Number of hourly paid staff
- Number of Monthly Paid Staff
- Total Number of Personnel
3.4) Production Quantities
It works integrated with sales and distributes the expense according to the amount of concrete produced by each plant. The following criteria are used.
- Pumped production quantity
- Production quantity without pump
- Total production quantity
3.5) Equal Distribution to Each Power Plant
3.6) Silobus Information
Silobus expenses are distributed according to the amount of tons carried by the plants.
3.7) User Requested Ratios
Distribution to the power plants: The user can make the distribution at the rates determined by the user.
4) Distribution Between Power Plants
If the costs of one power plant are increased because of other power plants, it is possible to allocate distribution shares among the power plants in a determined ratio and with keys in order to determine real and fair costs and profitability.
An accounting distribution slip is automatically generated using the distribution information mentioned above.
5) Cost Receipt
At the end of the month, an accounting receipt is automatically created on a plant basis to close the expense accounts and assign the expenses to the reflection accounts.
Standard Cost Operations
It is a dynamic application that enables businesses to see their future costs and profits by using the production information planned in the revenue budget and the methods determined in the expense budget, as well as user changes and forecasts.
In the structure of the expenditure budget, the following month’s costs are estimated Standard Cost called the “small budget application”. Don’t be fooled by how small it looks, its work is very big and important. This application is similar to a summer puzzle board. Users are able to see their future costs and profits. It has a dynamic structure.
For the near term, the production information planned in the income budget and the methods determined in the expense budget are taken. If desired, changes are made as desired according to the living structure and forecasting is made. Do not be afraid, your budgets will never change.
The person can see the cost, profit and break-even point of the near future close to reality.
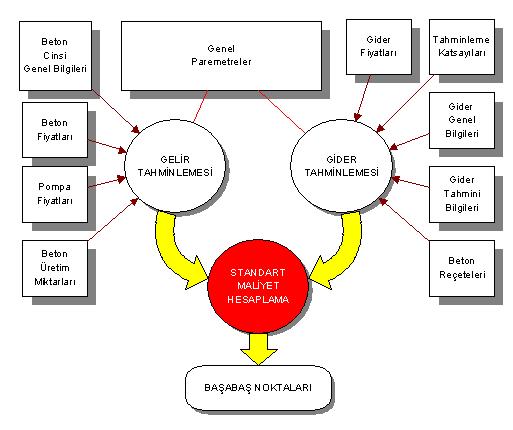
Thanks to this application, direction-action research can be carried out, the profit/loss trajectory in the near future can be foreseen and necessary measures can be taken. Break-even points of power plants can be identified and changes can be made in sales strategies if necessary. Employees can be motivated.
Costs can be calculated on concrete basis. In this way, problems in price determination are eliminated. It is possible to make estimates for large-scale projects and participate in tenders with the most favorable price. It is possible to estimate the profitability of the project.
Budget Transactions
It is very important for managers to forecast the future level of revenue, costs, expenses and to forecast cash flow accurately. POROShbs Budget is an application that meets all these expectations.
The budget is an indispensable process for managers. There are many reasons that make it necessary to forecast future revenue, costs and expenses, and to try to determine cash flow.
The budget is an indispensable process for managers. There are many reasons that make it necessary to predict the future level of income, costs and expenses, and to try to determine cash flow. With BİLTAŞ Budget application, budgeting has ceased to be just a bureaucratic process or a laborious and time-consuming year-end project that has become the fearful dream of employees. As you continue to navigate through the pages, you will find information about the Income Budget, Expense Budget, Standard Cost and Cash Flow modules under the Budget application.
Revenue Budget
It makes sense to put revenue forecasts first in the entire budgeting process. Thus, when creating the expenditure budget, variable expenditures will change based on revenue forecasts. The information obtained from this will be used for the cash flow and expense budget.
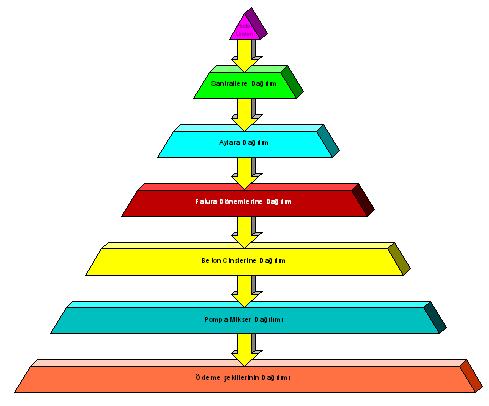
The revenue budget provides a detailed forecast of how the targeted concrete production amount for the planned year will be realized for each batching plant. For forecasting, ratios obtained through statistical studies using the production data of previous years are used. According to these ratios, the targeted production amount can be estimated in which batching plant, in which month and how much it will be, and even in the details of concrete type, pump and payment method.
Thanks to the ability to make budget forecasts in the detail of invoice periods and payment methods, it is easy to access information on the periods in which cash inflows will occur. The forecasted information can be changed proportionally and/or quantitatively in every desired detail.
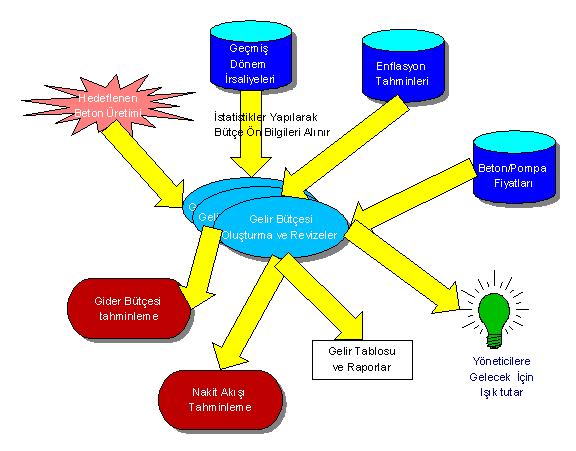
With its revizability feature, it provides the opportunity to create multiple revenue budgets and accordingly see the results that can be obtained with different criteria.
With the Revenue Budget module, you will no longer be intimidated by inflation; because the budget can work with annual or, if desired, monthly inflation. Thus, more realistic results will be achieved as price increases arising from inflation will also be taken into account.
The revenue budget is also available in foreign currency if desired.
The income budget consistency is made with current prices by using the discount determined in the budget. In this way, the turnover to be obtained for the future can be estimated and changes can be made in price and sales policies.
The production information realized in the revisions made during the year can also be monitored from the budget and the remaining months can be estimated. The calculated turnover comes closer to reality as the amount is based on current prices. By comparing the plan budget with the actual budget, deviations can be monitored and the budget can be made healthier by revising the estimates.
It is a fact that in real life there are many types of concrete and many payment methods for invoices. Instead of making separate estimates for each type of concrete and payment method in the budget, concrete types and payment methods are grouped and estimates are made according to these groups.
As mentioned earlier, information from the revenue budget is also used in the planned cash flow, in the estimation of variable (production-related) expenses in the expense budget and in the construction of the income statement.
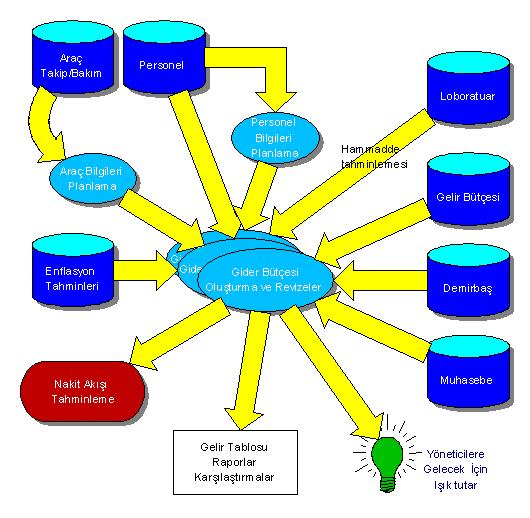
Expense Budget
With the expense budget module, the expenses to be incurred for the planned year are estimated. Expenses are estimated monthly according to power plants and production phases used in cost application.
Keys are set for expense estimation. The user performs the estimation by selecting the appropriate key for the expense. Revenue budget, laboratory, stock, inventory, fixture, cost, personnel, vehicle tracking and accounting applications are utilized for the estimation process.
The keys used in the system are as follows.
- Forecasting by Prescription:
It is used for estimating raw material costs. Using the production quantities taken from the income budget and concrete recipes taken from the laboratory application, the raw material quantities required for production are estimated. The raw material prices obtained from the stock can be changed by the user if desired, and the raw material expense information for the concrete to be produced is calculated.
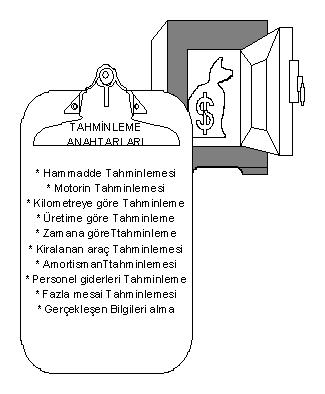
- Diesel Oil Forecasting : Diesel oil consumption information required for unit production is determined as a coefficient based on previous knowledge. With the help of this coefficient, diesel consumption is estimated depending on the production amount.
- Estimation by Mileage : Materials used for production, whose usage amount changes depending on the kilometers traveled, are estimated with this key. For example, vehicle tires are changed according to the mileage of the mixers. In the light of the information obtained from the vehicle tracking application, the mileage information for unit production is estimated as a coefficient. In addition, by estimating the number of kilometers every time the tires are changed, the tire cost is estimated according to the coefficients given depending on the production quantity.
- Estimation by Production Quantity : This key is used to estimate the materials directly used for production. Some materials become obsolete as production takes place and need to be replaced. Filters are a good example for this. Estimation will be estimated for total production for the material for which the information of how many units of production it has been changed for is known.
- Vehicle Rental Expenses Estimation : It is used for estimating the rental expenses of the power plants that rent vehicles. The number of vehicles to be rented is estimated. The calculation is made by considering the contribution share of the rented vehicles to the total production and using the rental fee.
- Estimation by Time : This key is used to estimate the materials that need to be changed in certain time periods. Estimation of the change period and quantity of the material according to the month is determined. Calculation is made in the light of this information.
- Estimating Fixed Expenses
- The actual information from accounting for the specified year is taken and the same values are used for the planned year.
- The monthly average of the accounting information realized for the specified period is taken and these values are used for each month of the plan year.
- Fixed values that can be determined separately for each power plant are used for each month.
- Depreciation Estimation :
It works integrated with the inventory application. If new fixture purchases are planned for the planned year, it is possible to make more realistic depreciation estimation by adding this fixture information.
- Estimation of Personnel Expenses:
Existing staff and average staff wages are taken from the personnel application. Plan, staff and wages can be obtained by making changes on it. By working integrated with the personnel application, personnel expenses such as wages, bonuses, SSK, savings incentive deductions are estimated.
Overtime can also be estimated. For this, the productivity coefficients of the staff are entered into the system and it is possible to estimate overtime based on the amount of production.
- New concrete plants to be built:
Expense estimation of new power plants can be made.
As with the revenue budget, it can be revised.
If desired, the budget can also work in foreign currency.
It can work with inflation. In fact, if desired, separate inflation forecasts can be made for each expense. In addition, if desired, increase coefficients can be defined for expenses.
When revised during the year, the actual information is taken from accounting. Forecasting for the coming months is done with current prices and other information to reach more realistic results.
Income statements are created using income and expenditure budgets.
It is possible to monitor expense budget information in the same structure where actual costs are monitored.
You can compare the plan with the reality.
You can compare budget revisions with each other.
You can compare the initial budget with the revisions.
You can compare the budgets of the power plants with each other.
Plant-based and company-wide budgets are prepared according to production phases. Unit cost estimation can also be made according to production estimates. Fixed and variable expense estimation can be made. It is possible to monitor phase cost estimates proportionally.
Monitoring the details of the phases; it is possible to group the expenses and access information according to the expense groups and, if desired, it is possible to go more detailed and access information up to the value of the expense incurred for the phase.
Estimated quantities of expenses quantified in accounting, usage amount and average price for unit production quantity can be monitored. This is especially important for monitoring raw material cost estimates.
Expense budget information is also used to generate the planned cash flow.
Cash Flow
The main purpose of budgeting is to obtain the necessary information for cash flow forecasting. One of the most important transactions for managers is cash flow. In this way, it will be able to see how much cash will be available in which periods. It will be seen whether there will be a cash bottleneck and necessary measures can be taken in advance. It is not always profitable to sell a lot, the important thing is to sell with favorable payment terms. Even if the sales made with high maturities show budget profitability, the real profitability is understood by cash flow.
Cash flow application estimates cash inflows and outflows according to the invoice periods in the light of the information obtained from income and expense budgets. The forecasting process is based on the due date for revenues and the estimated payment method for each expense for expenses.
In the realized cash flow, expenditures are calculated using the Payment Plan and cash inflows are calculated using Customer Current information. Thus, it is possible to compare the estimated and actual cash flow.
Instead of grouping expenditures and monitoring each expenditure cash flow separately, the total cash flow of expenditure groups can also be monitored.
General Accounting Transactions
It is an application where you can set up your accounting system according to special accounting periods, track your accounting transactions in original, local and standard currencies, support quantitative accounting as well as auxiliary accounts and expense location / expense type, income location / income type structure.
General Characteristics
- You can set up your accounting system according to special accounting periods and track your accounting transactions in original, local and standard currencies.
- You can define the account plan code structure according to the desired number of levels and get all reports based on each level you define.
- In addition to quantitative accounting, you can define auxiliary accounts and expense location/expense type, income location/income type structure and get reports according to this structure.
- You can perform line copying, receipt balance closing, column copying operations in order to provide ease of use and serial entry in receipt entries (offsetting, collection, disbursement, etc.).
- You can follow up the accounts according to the quantity units you specify in the accounts. You can monitor the quantity in the detailed reports that exist on the basis of trial balance, supplementary and account, and you can automatically get graphical images from all financial statement data created.
- You can optionally finalize integration receipts from different modules (inventory, fixed assets, personnel, etc.) automatically or in a controlled manner by collecting them in a data pool.
- You can quickly copy accounting slips or change the general properties of slips. By defining reflection accounts, you can create reflection receipts between the desired dates.
- You can create automatic closing and opening receipts at the end of the period.
- You can receive all legally valid books and reports (journal, ledger, general ledger, subsidiary ledger, balance sheet, income statement, fund flow statement, cash flow statement, e-statements, etc.) in different currencies.
Chart of Accounts
- You can organize the account plan code structure according to the desired number of levels and get all reports based on each level defined in the account.
- You can associate a defined account with expense locations and types.
- You can get reports about the expense location and type defined in the account.
- You can follow the account details that you do not want to be followed in the chart of accounts by defining auxiliary accounts. You can get trial balance and supplementary reports based on the defined auxiliary accounts.
- With the quantity units to be specified in the account definition, you can monitor the quantity in the trial balance, supplementary and detailed reports that exist on account basis.
- In order to provide ease of use and serial entry in receipt entries, you can perform line copying, receipt balance closing, column copying operations.
Accounting receipt transactions
- In order to provide ease of use and serial entry in receipt entries, you can perform line copying, receipt balance closing, column copying operations.
- You can track account receipt movements with the help of the expense location and expense type associated with the account.
- You can collect integration receipts from different modules in a data pool to control them and finalize them in a controlled manner.
- You can quickly copy accounting vouchers within the company or between group companies or change voucher general properties.
- By using different receipt numbering options, you can track your receipt numbers by Region, Year, Month, Day, receipt types.
- You can track accounting transactions in three different currencies (Local, Original, Standard) at the same time and get reports according to these currencies.
Financial reports
- You can prepare user-defined financial reports in the accounting system.
- You can automatically get graphical images from all generated financial statement data.
- You can generate financial reports in different currencies.
- You can automatically prepare financial statements such as balance sheet table, income statement, fund flow statement, cash flow statement on a period basis and between the desired dates, and report them according to the desired currency.
- You can get trial balance and balance according to the account breakdowns you want.
End of period transactions
- You can create an automatic closing/opening receipt at the end of the period.
- You can set up your accounting system according to special accounting periods and get all kinds of legal reports.
- You can automatically copy the automatically generated opening receipt to another company of your choice.
- You can perform official book shooting for control purposes without receiving official book transcripts.
Safe deposit operations
- Define cash registers according to different currencies within the Accounting System.
- You can automatically receive daily cash book reports for the defined cash registers.
Fixed Asset Transactions
In addition to the detailed and collective tracking of fixed assets registered in the enterprise, you can keep all the detailed information of the fixtures purchased through financial leasing in the system. You can also make depreciation and revaluation calculations, fixed asset purchase/sale details and embezzlement transactions. With this application;
- By opening a card for fixtures, you can track type, department, department code, purchase and sale information.
- You can provide fast entry by making inventory entries in bulk and on unit basis.
- You can follow the details of purchase and sale of fixtures and warranty expiries in detail.
- You can make and report embezzlement transactions to personnel.
- You can keep all the detailed information of the fixtures purchased through financial leasing in the system.
- You can make periodic depreciation calculations and offset them.
- You can get depreciation and revaluation ledgers by type, expense location and departments based on the entry date.
- You can make accounting integration of buying and selling transactions.
- In addition to ready-made reports, you can quickly prepare different reports thanks to the flexible reporting tool.
- Thanks to the accounting integration, you can automatically create offsets for purchase, sale and periodic depreciation amounts.
Personnel Transactions
It is an application where you can make personnel and accrual transactions (from gross to net, from net to gross) of your personnel working both in labor status and according to the 657 state civil servants law. With the difference payroll, you can create domestic and international travel, advance, seniority / notice, private health, etc. payrolls.
General Characteristics
- You can transfer the registry information of your personnel to the system in the most detailed way (including pictures).
- You can track and report all kinds of movements of your personnel within the organization (salary, duty, workplace, department, sub-department, etc.).
- You can create payrolls for domestic and international travel, advances, severance / notice, private health, difference, etc.
- You can make monthly accruals as gross to net and net to gross.
- You can prepare and send all kinds of legal reports as well as various declarations in electronic environment.
- You can run it fully integrated with different personnel attendance control systems and set up an automatic payroll generation structure.
- You can quickly make staff raises according to different formulas.
- You can make formula definitions on all income, deductions and discounts used in the payroll, and you can determine the calendars in which these income, deductions and discounts will be used and make them automatically active in the desired month.
- You can create an automatic offset of all payrolls made.
Personnel general operations
- You can define task codes hierarchically according to the organization chart in your organization.
- You can make formula definitions on all income, deductions and discounts that you will use in the payroll, and you can determine the calendar in which these income, deductions and discounts will be used and count them to be automatically output in the month you want.
- You can define reason codes for any changes made to the employee card.
- You can make all kinds of legal regulations and information changes parametrically.
- You can define wage payment information parameters and define the bank and currency of payment.
Personnel information
- You can make the wages and all other earnings of the personnel on a monthly, daily, hourly, net or gross basis according to the desired currency.
- You can separate your personnel by workplace, department, sub-department and payroll group to which they belong and get all your lists according to this information.
- In the personnel card, you can keep a lot of information about the personnel, from their personal information to all the schools they have attended to their favorite football team.
- You can see the history of retrospective salary, position, department, sub-department and workplace information changes of the personnel.
- You can make wage increases quickly according to the formula you will give.
- You can ensure that the information from the personnel attendance control system (PDKS) is automatically received into the system.
- If personnel payments are made through banks, you can prepare payment information according to the bank and branch where the personnel receive their salary and transmit it electronically.
- You can track employee family information in a detailed way.
- You can enter personnel union information and ensure that it is taken into account in all kinds of legal proceedings.
- You can track all embezzled and non-embezzled equipment given to the personnel, and you can also track the period and details of the in-kind aid given.
- You can make formal and informal leave plans for your company and report the leave book containing personnel leave information.
Personnel payroll information
- You can create any number and type of payrolls for the month.
- You can make formula definitions on all income, deductions and discounts that you will use in the payroll, and you can determine the calendar in which these income, deductions and discounts will be used and count them to be automatically output in the month you want.
- You can make the difference transactions of all payrolls made for the personnel, and you can ensure that the ssk declarations of these difference payrolls are received as additional declarations.
- Special expense deduction information can be tracked on an employee basis and these amounts can be reflected in the payrolls made during the month.
- You can create payroll and payroll in bulk between workplace department, sub-department, personnel group, personnel registration limits.
- You can track personnel debt and automatically reflect installment repayments to the payroll.
- If personnel payments are made through banks, you can prepare payment information according to the bank and branch where the personnel receive their salary and transmit it electronically.
- You can issue an advance payroll for the advance payments given to the personnel during the month.
- You can make domestic and international travel, severance, notice, private health payrolls.
- You can create automatic offset of all payrolls you make.
- In case the employee receives his/her salary from more than one company, you can distribute it by entering the distribution rates according to the companies and ensure that payment lists, declarations, etc. are received on a company basis.
- You can enter the missing days of the personnel and ensure that they are taken into account in the declarations.
Personnel reports
- You can report your personnel by workplace, department, subdivision and payroll group to which they belong.
- In addition to reporting general information of the personnel, you can get signature, address information reports.
- You can get icmal and detail reports of all personnel payrolls made.
- You can get reports of wage and task changes made on the personnel card.
- You can get horizontal and vertical payroll reports in the desired breakdown.
- You can get the staff health certificate together with your relatives.
- You can report personnel leave plans and leave books at any time.
- You can create a bank list for personnel payments.
Start Your Digital Transformation Journey with Biltaş
Meet smart software solutions that will optimize your business processes and increase your productivity.